Radiology: The Benefits Of Medical Monitor
Radiology is the medical specialty that, as the name says, uses radiation to make diagnoses and even treat some diseases. The doctor in this area is the radiologist who, after graduating in medicine, still performs medical residency in this specialty, lasting 3 to 6 years. In recent years the specialty has come to be known as radiology and imaging diagnosis due to the other tests and diagnoses it covers and does not necessarily make use of radiation, as is the case with ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging.
Who discovered the possibility of exploring the images formed by radiation was the German physicist Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen, who named the technique he named X-rays at the end of the 19th century. More than 100 years have passed, and radiology has expanded its possibilities for diagnosis and treatment with even more advanced techniques, such as computed tomography and mammography, for example.
Thanks to diagnostic imaging techniques today, it is possible to assess with great detail and precision clinical conditions that were not previously discovered or needed to be investigated in a more invasive way with exploratory surgeries. It allows diagnosing and measuring bone fractures, muscle injuries, tumors, neurological diseases, among other possibilities.
Benefits Of Medical Monitor
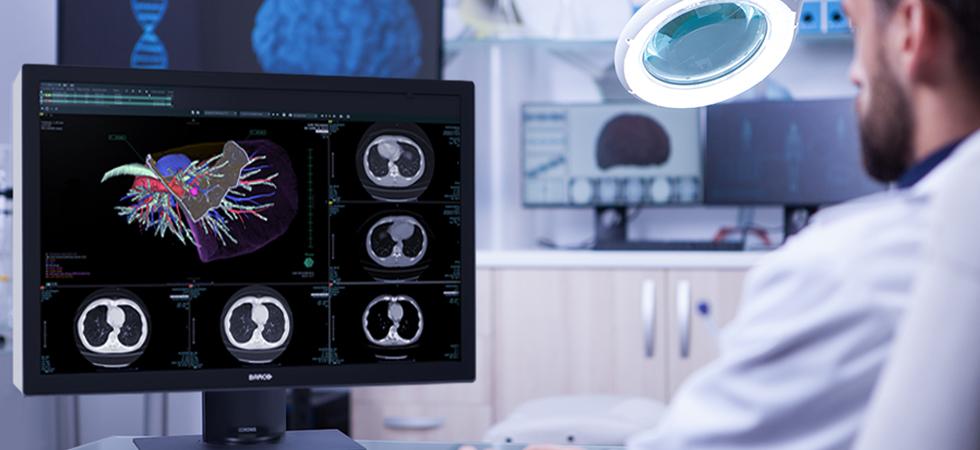
most health institutions use standard monitors to perform patient examinations. However, this equipment has some limitations that can influence the work of professionals, including negatively. Therefore, some places are opting for medical monitors for diagnosis.
The biggest benefit when using medical monitors for diagnosis is the image quality. A minimum monitor resolution is recommended for each imaging modality. For example, for tomography and resonance, 1 or 2 MB of resolution is enough. For an X-ray, you need at least 3 MB. In the case of mammography, this minimum resolution rises to 5 MB. The more complex the examination and the greater the image characteristics’ specificity, the more resolution will be required.
The orientation that medical monitors have, such as landscape or portrait viewing, also contributes to the radiologist having more details in the images and identifying possible injuries, improving the diagnosis.
Some medical monitors for diagnostics have DICOM calibration, which offers the appropriate characteristics for viewing images. Settings and other control tools are also essential features that are not found on conventional monitors.
Other aspects are also improved with medical monitors for diagnostics, such as grayscale, viewing angles, and contrast. Therefore, if your institution still uses common monitors, it is worth knowing the most specialized options available on the market.






