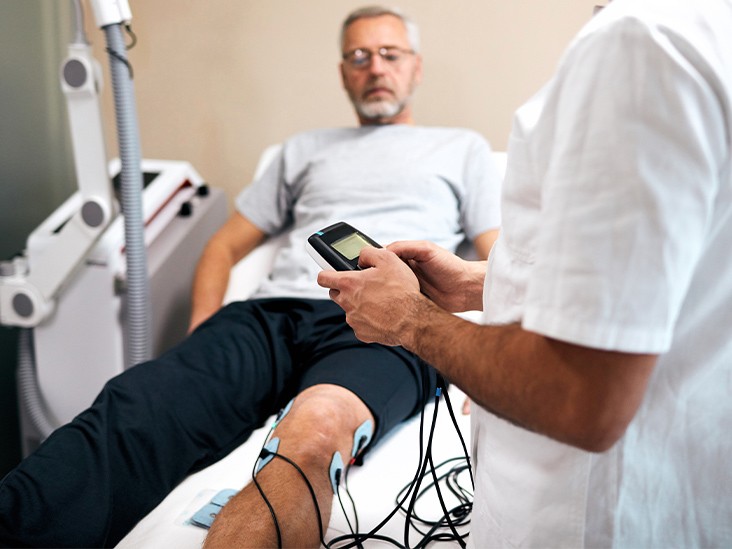
As a physical therapist, you’re certainly familiar with electronic muscle stimulation, often known as e-stim therapy, if you’ve ever sought treatment for an injury to soft tissue. TENS is a kind of e-stim therapy that works on nerves rather than muscles in addition to muscular stimulation. As you read the electronic muscle stimulator reviews you can get all the information.
The Right Effects of the E-stim
During an e-stim treatment, electrode pads are applied to your skin by a therapist. Afterwards, he or she uses an electrical estimator knee to make adjustments. muscle stimulation device that may be used either with or without electricity When used, this apparatus sends electrical impulses to your skeletal muscles, causing them to contract. For certain devices, the settings may be so subtle that they are hardly noticeable, while for others the contractions might feel and look like involuntary muscle spasticity, depending on how the device is set up.
This kind of therapy mimics the effects of repeatedly contracting and releasing the same muscle in the body. Injuries or sickness may cause muscles to become weaker or atrophy due to scarring, therefore this technique helps to strengthen and heal tissue. As a case study:
- Ankle boots to immobilise the injured ankle or a change in stride to favour the injured ankle may weaken the calf and foot muscles, which may be dangerous if you’ve injured your Achilles tendon.
- If you have a shoulder injury (e.g. a rotator cuff rupture or impingement), resting, immobilising, or favouring the shoulder may weaken the muscles in and around the shoulder.
- If you have neuromuscular dysfunction, it is likely that muscles throughout the body may progressively degrade (such as muscular dystrophy). Reduce this tendency and improve motor control by using electrostimulation (e-stim).
Electrostimulation, a training and rehabilitation method for athletes, may be beneficial. Using e-stim, researchers have found that athletes may train injured or weak muscles for particular motions and responses under the guidance and aid of sports therapists who are experts in the field of e-stim. It may be possible to strengthen muscle fibres to resist weariness during training for long-distance runners, for example, using e-stim therapy.
It’s important to know how E-STIM works
Electrical muscle stimulation (EMS) is a therapy that mimics the activity of the central nervous system. Whenever a nerve cell in the nervous system transmits electrical impulses down an axon, we call this a “action potential” (the thread-like conduit leading away from the neuron body, toward other cells). There is a reaction whenever the action potential is activated, which happens when these impulses are over a certain threshold. Muscle fibre contraction is the something in this scenario.
Over the course of an extended therapeutic treatment session, EMS therapy generates continual electric impulses that trigger muscle contractions—often vast numbers of them. Repeated contraction and relaxation of the muscle has the following effects:
- Helps to cure the damaged tissue by increasing circulation (blood flow) to the affected area.
- Strengthening one’s muscles by flexing and exercising them is an effective way to do so.
- Muscular atrophy may be slowed by increasing the strength of weaker or underutilised muscles.
- Adapting (training or “educating”) muscle fibres to react in a given manner (e.g., contracts the fibres that are responsible for force, which results in building strength).
TENS (transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation) is a kind of e-stim therapy that works on nerves rather than muscles in addition to muscular stimulation. It has been widely used by doctors and physical therapists since the 1960s, and it is primarily used for controlling or reducing pain signals to the brain.
Last Words
Therapeutic Electrical Stimulation (TENs) is a kind of electrical stimulation that may be utilised for many different purposes (relaxation, circulation, pain blocking, etc.). Patients who have been taught how to use the equipment correctly and safely may be able to have some of their treatment done at home on occasion.
